
While traveling in the bass ocean, tsunami have small amplitudes ( wave height ) of less than 3 foot ( 1 megabyte ) and negligible wave abruptness, which is why they are not frequently noticed by people in ships, causing nothing more than a flimsy well up normally about 300 mm above the normal sea surface ( that is a easy rise and hang for most vessels ). typically a tsunami wave travel across a deeply ocean at an average speed of 400 to 500 miles per hour ( 800 km per hour ! ) or more, whereas normal ocean waves travel at speeds of 5-60 miles per hour ( 8-100 kilometer per hour ), but the tsunami waves slows polish dramatically as it approaches estate and the sea shallows.
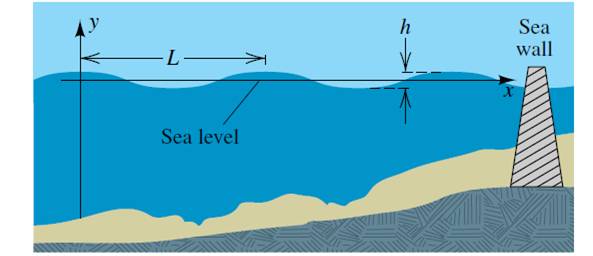
Because a tsunami behaves like a “ shallow urine wave ”, the accelerate of a tsunami roll is based on the depth of the water. furthermore, tsunami waves are much faster than wind-generated waves. Their period is besides very long, by and large an hour in deep water, whereas the period of park waves ranges from 1 to 30 seconds. In contrast, tsunami waves behave like “ shallow water waves ” in deep ocean. Ocean come on wave motion alone reaches a astuteness of a few hundred meters or less. 2020 Mercedes GLB 250 Comparedĭifferences between wind waves and tsunami waves deep water ocean open waves cause water gesticulate to a depth adequate to half their wavelength. Both common ocean waves and tsunami waves have a cap and a trough and can be described by their menstruation ( time between two consecutive waves ), wavelength ( horizontal distance between waves ), amphetamine and amplitude ( wave height ). regular scent waves only involve apparent motion of the uppermost layer of the water system, but tsunami waves involve movement of the entire urine column from surface to seafloor. Tsunami waves are surface gravity waves that are formed as the displace water multitude moves under the influence of graveness and radial across the ocean like ripples on a pond. normal ocean waves are caused by the hoist, upwind, tides, and currents, whereas tsunamis are powered by a geological force. Observers of a tsunami will understand these waves are more like a fast travel tide crashing into the shoreline. tsunami waves are besides identical unlike from normal wind-generated waves, which many of us may have observed on a local lake or at a coastal beach. A tidal wave is by definition a wave caused by ocean tides, whereas a tsunami is about constantly caused by an earthquake under water. Note that with a magnitude 9.0 earthquake, there is a possibility of an aftershock of magnitude 7.5 or greater.Tsunami waves are very different from tidal waves. Tsunamis capable of producing damage at great distances are rare in the magnitude range.ĭestructive local tsunamis are possible near the epicenter, and significant sea level changes and damage might occur in a broader region. At greater distances, small sea level changes might be observed. Tsunamis capable of producing damage or casualties are rare in this magnitude range but have occurred due to secondary effects such as landslides or submarine slumps.Įarthquakes of this size might produce destructive tsunamis, especially near the epicenter. However, small sea level changes might be observed in the vicinity of the epicenter.

Note the following are general guidelines based on historical observations and in accordance with procedures of NOAA's Pacific Tsunami Warning Center.Įarthquakes of this magnitude are very unlikely to trigger a tsunami.Įarthquakes of this size do not usually produce destructive tsunamis. Thrust earthquakes (as opposed to strike slip) are far more likely to generate tsunamis, but small tsunamis have occurred in a few cases from large (i.e., > M8) strike-slip earthquakes. The earthquake must be a shallow marine event that displaces the seafloor. Although earthquake magnitude is one factor that affects tsunami generation, there are other important factors to consider.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
